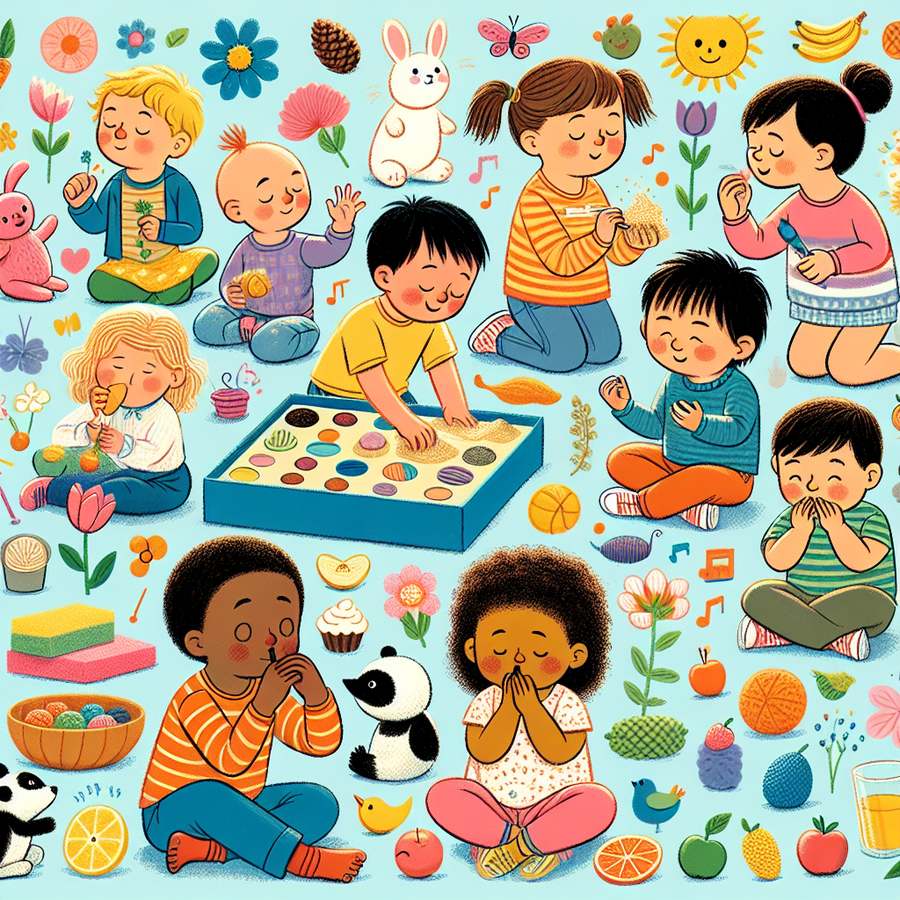
The role of sensory play in early childhood development cannot be overstated. It’s a fundamental way through which young children learn about their world. Sensory play includes any activity that stimulates a young child’s senses: touch, smell, taste, movement, balance, sight, and hearing. Through sensory play, children explore and naturally use scientific processes while they play, create, investigate, and explore.
The Importance of Sensory Play in Early Development
Sensory activities facilitate exploration and naturally encourage children to use scientific processes while they play, create, investigate, and explore. Engaging in sensory play helps to build nerve connections in the brain’s pathways. This leads to a child’s ability to complete more complex learning tasks and supports cognitive growth, language development, gross motor skills, social interaction, and problem-solving skills.
Furthermore, sensory play is crucial for the development of the senses themselves. As children interact with their environment, they develop sight, taste, touch, smell, and hearing. This development is vital for everyday tasks such as balance, movement, and effective communication skills. For more insights, this article delves deeper into the significance of sensory play.
Strategies for Incorporating Sensory Play
Introducing sensory play doesn’t have to be complicated. Simple activities like playing with dough, water play, and exploring textures with different materials can be incredibly beneficial. Parents and educators can create sensory bins filled with rice, beans, or water beads to allow children the freedom to explore tactile sensations.
Moreover, incorporating natural elements like sand, water, and garden play can significantly enhance sensory experiences. For those looking to support their child’s fine motor skills, consider activities like fine motor skill activities which are designed to improve hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
The Role of Sensory Play in Early Childhood Development
Sensory play supports language development too. As children describe their play, ask questions, and verbalize their actions, they develop language and communication skills. Sensory play also offers opportunities for children to interact socially. For instance, collaborative play in a sandbox encourages sharing, taking turns, and developing empathy among peers.
Significantly, sensory play aids in cognitive development and problem-solving. Activities such as building blocks, puzzles, and matching games that incorporate sensory elements can enhance memory, encourage scientific thinking, and support the understanding of cause and effect. For more ideas on enhancing cognitive skills through play, visit games for cognitive development.
In conclusion, the role of sensory play in early childhood development is pivotal. By engaging in sensory-rich activities, children develop fundamental skills necessary for their growth and learning. Parents and educators should strive to incorporate sensory play into daily activities, ensuring a well-rounded developmental experience for young children.
For additional resources on supporting your child’s development, explore our articles on the importance of touch in newborn development, encouraging self-feeding skills, and encouraging exploration and curiosity in infants.